What is Cloud Computing? Everything You Need to Know
Rohan Roy
Dec 9, 2024
Cloud Computing






Although it sounds complicated, cloud computing is a straightforward idea. It refers to keeping all of your crucial information, files, applications, and even servers on a huge web network known as the Cloud. It is hardly surprising that this forecast was made. It provides dependability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness-all essential for any business to expand and thrive.
Cloud technology computing is now the best means to offer enterprise apps and the go-to option for businesses looking to expand their infrastructure or introduce new ideas. Learn more about cloud computing by reading this cloud computing blog, which covers all you need to know, including its definition and frequently asked questions.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand, pay-per-use online access to computing resources, including virtual or physical servers, data storage, networking capabilities, software, application development tools, AI-powered analytical tools, and more. When it comes to scalability and flexibility, the cloud computing architecture outperforms traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Additionally, cloud computing can be separated into two layers that is front-end and back-end. The front-end layer is the layer that users usually interact with. This layer makes it possible for a user to use cloud computing applications to access data that has been saved in the cloud.
In simple terms, the on-demand provision of computer services, including servers, storage, database servers, networking purposes, software, and analytics, is known as cloud computing. Cloud-based storage enables remote file saving instead of storing data on a local storage device or proprietary hard disc. Because it offers cost savings, better productivity, speed and efficiency, efficiency, and security, cloud computing is a popular choice for both individuals and enterprises.
How does cloud computing work?
Through the internet, the client devices can access rented computer resources that include data, analytics, and cloud apps. all this is thanks to cloud computing. Cloud service providers own and run the network of distant data centers, servers, and storage devices that it depends on. The storage capacity, security, and processing power required to preserve the data users send to the cloud are the providers' responsibility.
Automation and virtualization technologies are key components of cloud computing. Through the use of software called a hypervisor, IT organizations can use virtualization to generate virtual instances of servers, storage, and other resources that enable numerous virtual machines (VMs) or cloud environments to operate on a single physical server.
This makes it easier for users to request and utilize cloud resources available. This is done by streamlining their abstraction and provisioning into logical entities. Without direct assistance from the cloud provider's IT team, users can provision resources, connect services, and deploy workloads with a high degree of self-service thanks to automation and related orchestration features.
Types of cloud services
Private cloud
Internal users can use private cloud services from a company's data center. An organization creates and manages its own underlying cloud architecture when using a private cloud. This paradigm maintains the administration, control, and security typical of local data centers while providing the flexibility and convenience of the cloud. OpenStack and VMware are two examples of private cloud suppliers and technologies.
To satisfy their regulatory compliance needs, many businesses opt for private cloud environments rather than public ones. Private cloud environments are frequently chosen by organizations such as government agencies, healthcare facilities, and financial institutions for workloads including sensitive data, medical records, intellectual property, private documents, personally identifiable information (PII), and financial information.
Public cloud
A third-party cloud service provider (CSP) provides the cloud service online. That too under the public cloud paradigm. Although many public cloud services offer long-term commitments, they are usually sold on a minute or hourly basis. Consumers just pay for the bandwidth of the cloud, data storage, and CPU cycles that they usually use.
Since public cloud services are easily scalable and elastic, most businesses have shifted parts of their computer infrastructure to the cloud. This allows them to adapt to changing workload demands. Customers are drawn to the public cloud by the promise of increased efficiency and cost savings by only paying for what they use.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud combines on-premises private cloud services. This is with public cloud services that include automation and orchestration between the two types of cloud. Businesses can use the public cloud to manage their daily demand spikes or workload bursts. They can also use it while running sensitive apps or important workloads on the private cloud.
Creating a unified, automated, scalable environment that utilizes everything that a public cloud architecture has to offer while retaining control over mission-critical data is the aim of a hybrid cloud. Beyond physical connectivity and cloud migration, hybrid cloud architecture now provides a cost-effective, adaptable, and secure environment that facilitates workload portability and automated deployment across many environments.
Benefits of cloud computing
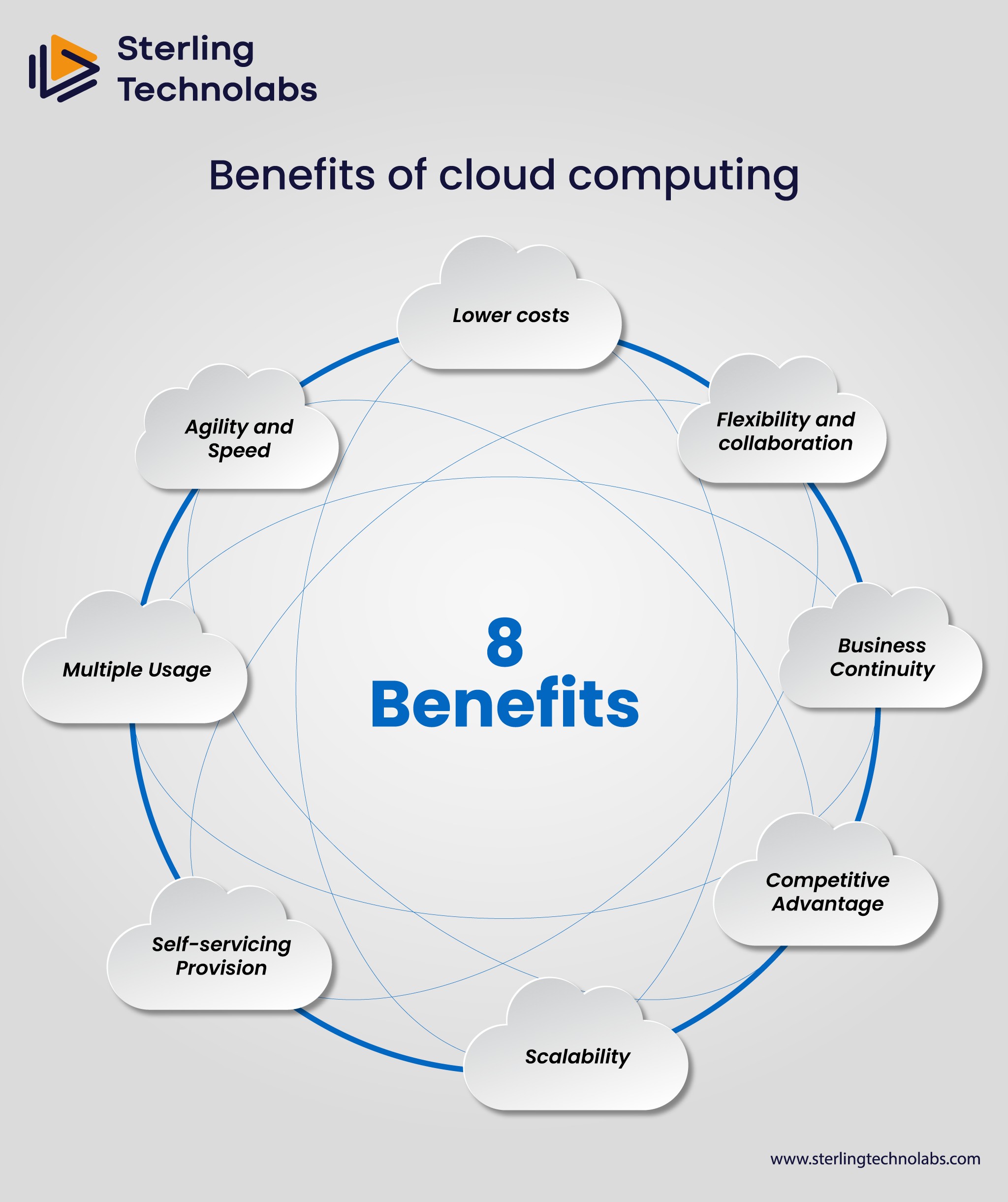
Lower costs
IT cloud computing helps lower the large capital expenditures needed to maintain IT systems. Businesses can significantly cut costs by utilizing the capabilities offered by the cloud provider instead of investing in pricey infrastructure. Businesses only pay for the services they utilize thanks to cloud providers' pay-as-you-go business model, which further lowers expenses.
Flexibility and collaboration
Employees can work from anywhere at any time since cloud data is instantly accessible over the internet. You can set up your virtual workplace from anywhere thanks to the cloud. By granting them access to the same files as outside vendors, it also enables teams to collaborate on a project from different places.
Business Continuity
In the case of an emergency or outage, your data is securely stored and safeguarded in the cloud. When the systems are back up and running, this facilitates getting back to work.
Competitive Advantage
Cloud handles a number of corporate functions, including software licensing, IT infrastructure maintenance, and data management training staff. As a result, it offers you a competitive advantage because it requires less time and money.
Scalability
Cloud computing enables businesses to quickly expand their user base from a small number to thousands. Businesses can scale their storage requirements based on their need that gives them flexibility.
Self-servicing Provision
End users can request compute resources for almost any type of workload. End users can now provision computing capabilities such as server time and network storage, eliminating the need for IT administrators to provision and manage compute resources.
Multiple Usage
With multi-tenancy, several clients can share the same apps or physical infrastructures while maintaining control over their personal information security and privacy. Cloud providers can serve several clients from the same physical resources by using resource pooling. In order to meet the needs of numerous clients, cloud providers need have sizable and adaptable resource pools.
Agility and Speed
Rapid application and service deployment is made possible by cloud computing, which enables developers to quickly create resources and test new concepts. This speeds up time to market by doing away with the requirement for laborious hardware procurement procedures.
What are the future trends?
Container technology popularity
Container technology will become more and more popular over time. Regardless of the parent hosting environment (cloud, hybrid, or on-premise servers), containers provide a separate virtual environment for developing and executing applications. In essence, it enables businesses to enhance their development capabilities by establishing small, isolated clouds inside their own infrastructure.
The use of virtual desktops
It will grow in popularity and acceptance. Without connecting the desktop to the actual client device, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) enables remote desktop picture streaming. Since apps and services may be readily distributed to a distant client without requiring complicated installation or configuration, remote worker productivity is a key use case for virtual desktop infrastructure.
Security technologies
It will advance to become edge-first and cloud-native. The decentralization of remote hosting and processing via edge infrastructure is a key component of cloud evolution. The edge is the next frontier, even if cloud computing was previously a priority for cybersecurity companies since shared resources entail shared security threats.
Cloud use cases
These involve communication and collaboration will be crucial.
Following the widespread transition to remote work in 2020, modernizing channels for cooperation and communication was one of the top goals. Businesses may connect remotely thanks to the cloud, which makes it easier to collaborate within and interact with customers externally. VoIP and cloud-based video conferencing aren't the only examples of this.
Serverless computing
Even outside of the tech industry, serverless computing will be a fascinating area of adoption. A form of enterprise IT design where code is separated and modular is made possible by serverless architecture. It is an execution model that is usually used for cloud computing Such that in which resources are allocated to each isolated module that too based on real-time demand. Serverless is usually only used by platform providers and IT organizations who need to guarantee the highest amount of downtime for their products.
Cloud will drive the broad use of AI
Demand for artificial intelligence (AI) is rising in all business verticals and horizontals. Adoption of cloud computing will depend on the availability of AI libraries, modelling engines, and algorithms stored in the cloud.
Conclusion
It is anticipated that this investigation of cloud computing's characteristics will increase its capacity to revolutionize your company. We've talked about its wide range of products, how to match them to your unique requirements, and the technology's bright future.
Better methods for developing goods and services, giving good customer support, and doing research will be easily made possible by the cloud in the future. Business executives that take advantage of cloud computing's possibilities will undoubtedly have an advantage over their competitors in this dynamic environment, whether it be in the software and tools selected or the business plans they implement.
It might be very difficult to choose the best cloud option for your company. It's simple to become overwhelmed by the abundance of possibilities, particularly when your company's needs are changing and becoming more specific. To help you make the best choice in this situation, you require cloud consulting services at Sterling Technolabs.

FAQs
Q: What is Cloud Computing and How Does It Work?
A: Users can pay for just the computing resources that they use with the cloud computing. This is what it makes computing resources available over the internet as needed. It gives users access to technological services as needed, doing away with the need to maintain physical resources like servers and data centres.
Q: What Are the Different Types of Cloud Computing?
A: Public, private, and hybrid clouds are the three primary categories of cloud computing. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and serverless computing are the four primary services that fall under these deployment patterns.
Q: What Are the Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses?
A: Increased performance and efficiency, greater flexibility and dependability, and reduced IT expenses are all provided by the cloud. Additionally, it enhances innovation, enabling businesses to integrate AI and machine learning applications into their strategy and get a quicker time to market.
Q: What Are Cloud Computing Services?
A: Servers, storage, database servers, networking, software, statistical analysis, and intelligence are examples of computer resources that are made available online as cloud computing services. Without having to handle physical resources directly, cloud computing services enable both individuals and enterprises to access computing resources whenever they need them.
Q: What Are the Challenges of Cloud Computing?
A: The major challenges in cloud computing are serves, technology, usage issues, data security, performance, control, expertise and much more that are seen when used.
Although it sounds complicated, cloud computing is a straightforward idea. It refers to keeping all of your crucial information, files, applications, and even servers on a huge web network known as the Cloud. It is hardly surprising that this forecast was made. It provides dependability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness-all essential for any business to expand and thrive.
Cloud technology computing is now the best means to offer enterprise apps and the go-to option for businesses looking to expand their infrastructure or introduce new ideas. Learn more about cloud computing by reading this cloud computing blog, which covers all you need to know, including its definition and frequently asked questions.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand, pay-per-use online access to computing resources, including virtual or physical servers, data storage, networking capabilities, software, application development tools, AI-powered analytical tools, and more. When it comes to scalability and flexibility, the cloud computing architecture outperforms traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Additionally, cloud computing can be separated into two layers that is front-end and back-end. The front-end layer is the layer that users usually interact with. This layer makes it possible for a user to use cloud computing applications to access data that has been saved in the cloud.
In simple terms, the on-demand provision of computer services, including servers, storage, database servers, networking purposes, software, and analytics, is known as cloud computing. Cloud-based storage enables remote file saving instead of storing data on a local storage device or proprietary hard disc. Because it offers cost savings, better productivity, speed and efficiency, efficiency, and security, cloud computing is a popular choice for both individuals and enterprises.
How does cloud computing work?
Through the internet, the client devices can access rented computer resources that include data, analytics, and cloud apps. all this is thanks to cloud computing. Cloud service providers own and run the network of distant data centers, servers, and storage devices that it depends on. The storage capacity, security, and processing power required to preserve the data users send to the cloud are the providers' responsibility.
Automation and virtualization technologies are key components of cloud computing. Through the use of software called a hypervisor, IT organizations can use virtualization to generate virtual instances of servers, storage, and other resources that enable numerous virtual machines (VMs) or cloud environments to operate on a single physical server.
This makes it easier for users to request and utilize cloud resources available. This is done by streamlining their abstraction and provisioning into logical entities. Without direct assistance from the cloud provider's IT team, users can provision resources, connect services, and deploy workloads with a high degree of self-service thanks to automation and related orchestration features.
Types of cloud services
Private cloud
Internal users can use private cloud services from a company's data center. An organization creates and manages its own underlying cloud architecture when using a private cloud. This paradigm maintains the administration, control, and security typical of local data centers while providing the flexibility and convenience of the cloud. OpenStack and VMware are two examples of private cloud suppliers and technologies.
To satisfy their regulatory compliance needs, many businesses opt for private cloud environments rather than public ones. Private cloud environments are frequently chosen by organizations such as government agencies, healthcare facilities, and financial institutions for workloads including sensitive data, medical records, intellectual property, private documents, personally identifiable information (PII), and financial information.
Public cloud
A third-party cloud service provider (CSP) provides the cloud service online. That too under the public cloud paradigm. Although many public cloud services offer long-term commitments, they are usually sold on a minute or hourly basis. Consumers just pay for the bandwidth of the cloud, data storage, and CPU cycles that they usually use.
Since public cloud services are easily scalable and elastic, most businesses have shifted parts of their computer infrastructure to the cloud. This allows them to adapt to changing workload demands. Customers are drawn to the public cloud by the promise of increased efficiency and cost savings by only paying for what they use.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud combines on-premises private cloud services. This is with public cloud services that include automation and orchestration between the two types of cloud. Businesses can use the public cloud to manage their daily demand spikes or workload bursts. They can also use it while running sensitive apps or important workloads on the private cloud.
Creating a unified, automated, scalable environment that utilizes everything that a public cloud architecture has to offer while retaining control over mission-critical data is the aim of a hybrid cloud. Beyond physical connectivity and cloud migration, hybrid cloud architecture now provides a cost-effective, adaptable, and secure environment that facilitates workload portability and automated deployment across many environments.
Benefits of cloud computing

Lower costs
IT cloud computing helps lower the large capital expenditures needed to maintain IT systems. Businesses can significantly cut costs by utilizing the capabilities offered by the cloud provider instead of investing in pricey infrastructure. Businesses only pay for the services they utilize thanks to cloud providers' pay-as-you-go business model, which further lowers expenses.
Flexibility and collaboration
Employees can work from anywhere at any time since cloud data is instantly accessible over the internet. You can set up your virtual workplace from anywhere thanks to the cloud. By granting them access to the same files as outside vendors, it also enables teams to collaborate on a project from different places.
Business Continuity
In the case of an emergency or outage, your data is securely stored and safeguarded in the cloud. When the systems are back up and running, this facilitates getting back to work.
Competitive Advantage
Cloud handles a number of corporate functions, including software licensing, IT infrastructure maintenance, and data management training staff. As a result, it offers you a competitive advantage because it requires less time and money.
Scalability
Cloud computing enables businesses to quickly expand their user base from a small number to thousands. Businesses can scale their storage requirements based on their need that gives them flexibility.
Self-servicing Provision
End users can request compute resources for almost any type of workload. End users can now provision computing capabilities such as server time and network storage, eliminating the need for IT administrators to provision and manage compute resources.
Multiple Usage
With multi-tenancy, several clients can share the same apps or physical infrastructures while maintaining control over their personal information security and privacy. Cloud providers can serve several clients from the same physical resources by using resource pooling. In order to meet the needs of numerous clients, cloud providers need have sizable and adaptable resource pools.
Agility and Speed
Rapid application and service deployment is made possible by cloud computing, which enables developers to quickly create resources and test new concepts. This speeds up time to market by doing away with the requirement for laborious hardware procurement procedures.
What are the future trends?
Container technology popularity
Container technology will become more and more popular over time. Regardless of the parent hosting environment (cloud, hybrid, or on-premise servers), containers provide a separate virtual environment for developing and executing applications. In essence, it enables businesses to enhance their development capabilities by establishing small, isolated clouds inside their own infrastructure.
The use of virtual desktops
It will grow in popularity and acceptance. Without connecting the desktop to the actual client device, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) enables remote desktop picture streaming. Since apps and services may be readily distributed to a distant client without requiring complicated installation or configuration, remote worker productivity is a key use case for virtual desktop infrastructure.
Security technologies
It will advance to become edge-first and cloud-native. The decentralization of remote hosting and processing via edge infrastructure is a key component of cloud evolution. The edge is the next frontier, even if cloud computing was previously a priority for cybersecurity companies since shared resources entail shared security threats.
Cloud use cases
These involve communication and collaboration will be crucial.
Following the widespread transition to remote work in 2020, modernizing channels for cooperation and communication was one of the top goals. Businesses may connect remotely thanks to the cloud, which makes it easier to collaborate within and interact with customers externally. VoIP and cloud-based video conferencing aren't the only examples of this.
Serverless computing
Even outside of the tech industry, serverless computing will be a fascinating area of adoption. A form of enterprise IT design where code is separated and modular is made possible by serverless architecture. It is an execution model that is usually used for cloud computing Such that in which resources are allocated to each isolated module that too based on real-time demand. Serverless is usually only used by platform providers and IT organizations who need to guarantee the highest amount of downtime for their products.
Cloud will drive the broad use of AI
Demand for artificial intelligence (AI) is rising in all business verticals and horizontals. Adoption of cloud computing will depend on the availability of AI libraries, modelling engines, and algorithms stored in the cloud.
Conclusion
It is anticipated that this investigation of cloud computing's characteristics will increase its capacity to revolutionize your company. We've talked about its wide range of products, how to match them to your unique requirements, and the technology's bright future.
Better methods for developing goods and services, giving good customer support, and doing research will be easily made possible by the cloud in the future. Business executives that take advantage of cloud computing's possibilities will undoubtedly have an advantage over their competitors in this dynamic environment, whether it be in the software and tools selected or the business plans they implement.
It might be very difficult to choose the best cloud option for your company. It's simple to become overwhelmed by the abundance of possibilities, particularly when your company's needs are changing and becoming more specific. To help you make the best choice in this situation, you require cloud consulting services at Sterling Technolabs.

FAQs
Q: What is Cloud Computing and How Does It Work?
A: Users can pay for just the computing resources that they use with the cloud computing. This is what it makes computing resources available over the internet as needed. It gives users access to technological services as needed, doing away with the need to maintain physical resources like servers and data centres.
Q: What Are the Different Types of Cloud Computing?
A: Public, private, and hybrid clouds are the three primary categories of cloud computing. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and serverless computing are the four primary services that fall under these deployment patterns.
Q: What Are the Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses?
A: Increased performance and efficiency, greater flexibility and dependability, and reduced IT expenses are all provided by the cloud. Additionally, it enhances innovation, enabling businesses to integrate AI and machine learning applications into their strategy and get a quicker time to market.
Q: What Are Cloud Computing Services?
A: Servers, storage, database servers, networking, software, statistical analysis, and intelligence are examples of computer resources that are made available online as cloud computing services. Without having to handle physical resources directly, cloud computing services enable both individuals and enterprises to access computing resources whenever they need them.
Q: What Are the Challenges of Cloud Computing?
A: The major challenges in cloud computing are serves, technology, usage issues, data security, performance, control, expertise and much more that are seen when used.
Although it sounds complicated, cloud computing is a straightforward idea. It refers to keeping all of your crucial information, files, applications, and even servers on a huge web network known as the Cloud. It is hardly surprising that this forecast was made. It provides dependability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness-all essential for any business to expand and thrive.
Cloud technology computing is now the best means to offer enterprise apps and the go-to option for businesses looking to expand their infrastructure or introduce new ideas. Learn more about cloud computing by reading this cloud computing blog, which covers all you need to know, including its definition and frequently asked questions.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand, pay-per-use online access to computing resources, including virtual or physical servers, data storage, networking capabilities, software, application development tools, AI-powered analytical tools, and more. When it comes to scalability and flexibility, the cloud computing architecture outperforms traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Additionally, cloud computing can be separated into two layers that is front-end and back-end. The front-end layer is the layer that users usually interact with. This layer makes it possible for a user to use cloud computing applications to access data that has been saved in the cloud.
In simple terms, the on-demand provision of computer services, including servers, storage, database servers, networking purposes, software, and analytics, is known as cloud computing. Cloud-based storage enables remote file saving instead of storing data on a local storage device or proprietary hard disc. Because it offers cost savings, better productivity, speed and efficiency, efficiency, and security, cloud computing is a popular choice for both individuals and enterprises.
How does cloud computing work?
Through the internet, the client devices can access rented computer resources that include data, analytics, and cloud apps. all this is thanks to cloud computing. Cloud service providers own and run the network of distant data centers, servers, and storage devices that it depends on. The storage capacity, security, and processing power required to preserve the data users send to the cloud are the providers' responsibility.
Automation and virtualization technologies are key components of cloud computing. Through the use of software called a hypervisor, IT organizations can use virtualization to generate virtual instances of servers, storage, and other resources that enable numerous virtual machines (VMs) or cloud environments to operate on a single physical server.
This makes it easier for users to request and utilize cloud resources available. This is done by streamlining their abstraction and provisioning into logical entities. Without direct assistance from the cloud provider's IT team, users can provision resources, connect services, and deploy workloads with a high degree of self-service thanks to automation and related orchestration features.
Types of cloud services
Private cloud
Internal users can use private cloud services from a company's data center. An organization creates and manages its own underlying cloud architecture when using a private cloud. This paradigm maintains the administration, control, and security typical of local data centers while providing the flexibility and convenience of the cloud. OpenStack and VMware are two examples of private cloud suppliers and technologies.
To satisfy their regulatory compliance needs, many businesses opt for private cloud environments rather than public ones. Private cloud environments are frequently chosen by organizations such as government agencies, healthcare facilities, and financial institutions for workloads including sensitive data, medical records, intellectual property, private documents, personally identifiable information (PII), and financial information.
Public cloud
A third-party cloud service provider (CSP) provides the cloud service online. That too under the public cloud paradigm. Although many public cloud services offer long-term commitments, they are usually sold on a minute or hourly basis. Consumers just pay for the bandwidth of the cloud, data storage, and CPU cycles that they usually use.
Since public cloud services are easily scalable and elastic, most businesses have shifted parts of their computer infrastructure to the cloud. This allows them to adapt to changing workload demands. Customers are drawn to the public cloud by the promise of increased efficiency and cost savings by only paying for what they use.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud combines on-premises private cloud services. This is with public cloud services that include automation and orchestration between the two types of cloud. Businesses can use the public cloud to manage their daily demand spikes or workload bursts. They can also use it while running sensitive apps or important workloads on the private cloud.
Creating a unified, automated, scalable environment that utilizes everything that a public cloud architecture has to offer while retaining control over mission-critical data is the aim of a hybrid cloud. Beyond physical connectivity and cloud migration, hybrid cloud architecture now provides a cost-effective, adaptable, and secure environment that facilitates workload portability and automated deployment across many environments.
Benefits of cloud computing

Lower costs
IT cloud computing helps lower the large capital expenditures needed to maintain IT systems. Businesses can significantly cut costs by utilizing the capabilities offered by the cloud provider instead of investing in pricey infrastructure. Businesses only pay for the services they utilize thanks to cloud providers' pay-as-you-go business model, which further lowers expenses.
Flexibility and collaboration
Employees can work from anywhere at any time since cloud data is instantly accessible over the internet. You can set up your virtual workplace from anywhere thanks to the cloud. By granting them access to the same files as outside vendors, it also enables teams to collaborate on a project from different places.
Business Continuity
In the case of an emergency or outage, your data is securely stored and safeguarded in the cloud. When the systems are back up and running, this facilitates getting back to work.
Competitive Advantage
Cloud handles a number of corporate functions, including software licensing, IT infrastructure maintenance, and data management training staff. As a result, it offers you a competitive advantage because it requires less time and money.
Scalability
Cloud computing enables businesses to quickly expand their user base from a small number to thousands. Businesses can scale their storage requirements based on their need that gives them flexibility.
Self-servicing Provision
End users can request compute resources for almost any type of workload. End users can now provision computing capabilities such as server time and network storage, eliminating the need for IT administrators to provision and manage compute resources.
Multiple Usage
With multi-tenancy, several clients can share the same apps or physical infrastructures while maintaining control over their personal information security and privacy. Cloud providers can serve several clients from the same physical resources by using resource pooling. In order to meet the needs of numerous clients, cloud providers need have sizable and adaptable resource pools.
Agility and Speed
Rapid application and service deployment is made possible by cloud computing, which enables developers to quickly create resources and test new concepts. This speeds up time to market by doing away with the requirement for laborious hardware procurement procedures.
What are the future trends?
Container technology popularity
Container technology will become more and more popular over time. Regardless of the parent hosting environment (cloud, hybrid, or on-premise servers), containers provide a separate virtual environment for developing and executing applications. In essence, it enables businesses to enhance their development capabilities by establishing small, isolated clouds inside their own infrastructure.
The use of virtual desktops
It will grow in popularity and acceptance. Without connecting the desktop to the actual client device, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) enables remote desktop picture streaming. Since apps and services may be readily distributed to a distant client without requiring complicated installation or configuration, remote worker productivity is a key use case for virtual desktop infrastructure.
Security technologies
It will advance to become edge-first and cloud-native. The decentralization of remote hosting and processing via edge infrastructure is a key component of cloud evolution. The edge is the next frontier, even if cloud computing was previously a priority for cybersecurity companies since shared resources entail shared security threats.
Cloud use cases
These involve communication and collaboration will be crucial.
Following the widespread transition to remote work in 2020, modernizing channels for cooperation and communication was one of the top goals. Businesses may connect remotely thanks to the cloud, which makes it easier to collaborate within and interact with customers externally. VoIP and cloud-based video conferencing aren't the only examples of this.
Serverless computing
Even outside of the tech industry, serverless computing will be a fascinating area of adoption. A form of enterprise IT design where code is separated and modular is made possible by serverless architecture. It is an execution model that is usually used for cloud computing Such that in which resources are allocated to each isolated module that too based on real-time demand. Serverless is usually only used by platform providers and IT organizations who need to guarantee the highest amount of downtime for their products.
Cloud will drive the broad use of AI
Demand for artificial intelligence (AI) is rising in all business verticals and horizontals. Adoption of cloud computing will depend on the availability of AI libraries, modelling engines, and algorithms stored in the cloud.
Conclusion
It is anticipated that this investigation of cloud computing's characteristics will increase its capacity to revolutionize your company. We've talked about its wide range of products, how to match them to your unique requirements, and the technology's bright future.
Better methods for developing goods and services, giving good customer support, and doing research will be easily made possible by the cloud in the future. Business executives that take advantage of cloud computing's possibilities will undoubtedly have an advantage over their competitors in this dynamic environment, whether it be in the software and tools selected or the business plans they implement.
It might be very difficult to choose the best cloud option for your company. It's simple to become overwhelmed by the abundance of possibilities, particularly when your company's needs are changing and becoming more specific. To help you make the best choice in this situation, you require cloud consulting services at Sterling Technolabs.

FAQs
Q: What is Cloud Computing and How Does It Work?
A: Users can pay for just the computing resources that they use with the cloud computing. This is what it makes computing resources available over the internet as needed. It gives users access to technological services as needed, doing away with the need to maintain physical resources like servers and data centres.
Q: What Are the Different Types of Cloud Computing?
A: Public, private, and hybrid clouds are the three primary categories of cloud computing. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and serverless computing are the four primary services that fall under these deployment patterns.
Q: What Are the Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses?
A: Increased performance and efficiency, greater flexibility and dependability, and reduced IT expenses are all provided by the cloud. Additionally, it enhances innovation, enabling businesses to integrate AI and machine learning applications into their strategy and get a quicker time to market.
Q: What Are Cloud Computing Services?
A: Servers, storage, database servers, networking, software, statistical analysis, and intelligence are examples of computer resources that are made available online as cloud computing services. Without having to handle physical resources directly, cloud computing services enable both individuals and enterprises to access computing resources whenever they need them.
Q: What Are the Challenges of Cloud Computing?
A: The major challenges in cloud computing are serves, technology, usage issues, data security, performance, control, expertise and much more that are seen when used.
Although it sounds complicated, cloud computing is a straightforward idea. It refers to keeping all of your crucial information, files, applications, and even servers on a huge web network known as the Cloud. It is hardly surprising that this forecast was made. It provides dependability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness-all essential for any business to expand and thrive.
Cloud technology computing is now the best means to offer enterprise apps and the go-to option for businesses looking to expand their infrastructure or introduce new ideas. Learn more about cloud computing by reading this cloud computing blog, which covers all you need to know, including its definition and frequently asked questions.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand, pay-per-use online access to computing resources, including virtual or physical servers, data storage, networking capabilities, software, application development tools, AI-powered analytical tools, and more. When it comes to scalability and flexibility, the cloud computing architecture outperforms traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Additionally, cloud computing can be separated into two layers that is front-end and back-end. The front-end layer is the layer that users usually interact with. This layer makes it possible for a user to use cloud computing applications to access data that has been saved in the cloud.
In simple terms, the on-demand provision of computer services, including servers, storage, database servers, networking purposes, software, and analytics, is known as cloud computing. Cloud-based storage enables remote file saving instead of storing data on a local storage device or proprietary hard disc. Because it offers cost savings, better productivity, speed and efficiency, efficiency, and security, cloud computing is a popular choice for both individuals and enterprises.
How does cloud computing work?
Through the internet, the client devices can access rented computer resources that include data, analytics, and cloud apps. all this is thanks to cloud computing. Cloud service providers own and run the network of distant data centers, servers, and storage devices that it depends on. The storage capacity, security, and processing power required to preserve the data users send to the cloud are the providers' responsibility.
Automation and virtualization technologies are key components of cloud computing. Through the use of software called a hypervisor, IT organizations can use virtualization to generate virtual instances of servers, storage, and other resources that enable numerous virtual machines (VMs) or cloud environments to operate on a single physical server.
This makes it easier for users to request and utilize cloud resources available. This is done by streamlining their abstraction and provisioning into logical entities. Without direct assistance from the cloud provider's IT team, users can provision resources, connect services, and deploy workloads with a high degree of self-service thanks to automation and related orchestration features.
Types of cloud services
Private cloud
Internal users can use private cloud services from a company's data center. An organization creates and manages its own underlying cloud architecture when using a private cloud. This paradigm maintains the administration, control, and security typical of local data centers while providing the flexibility and convenience of the cloud. OpenStack and VMware are two examples of private cloud suppliers and technologies.
To satisfy their regulatory compliance needs, many businesses opt for private cloud environments rather than public ones. Private cloud environments are frequently chosen by organizations such as government agencies, healthcare facilities, and financial institutions for workloads including sensitive data, medical records, intellectual property, private documents, personally identifiable information (PII), and financial information.
Public cloud
A third-party cloud service provider (CSP) provides the cloud service online. That too under the public cloud paradigm. Although many public cloud services offer long-term commitments, they are usually sold on a minute or hourly basis. Consumers just pay for the bandwidth of the cloud, data storage, and CPU cycles that they usually use.
Since public cloud services are easily scalable and elastic, most businesses have shifted parts of their computer infrastructure to the cloud. This allows them to adapt to changing workload demands. Customers are drawn to the public cloud by the promise of increased efficiency and cost savings by only paying for what they use.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud combines on-premises private cloud services. This is with public cloud services that include automation and orchestration between the two types of cloud. Businesses can use the public cloud to manage their daily demand spikes or workload bursts. They can also use it while running sensitive apps or important workloads on the private cloud.
Creating a unified, automated, scalable environment that utilizes everything that a public cloud architecture has to offer while retaining control over mission-critical data is the aim of a hybrid cloud. Beyond physical connectivity and cloud migration, hybrid cloud architecture now provides a cost-effective, adaptable, and secure environment that facilitates workload portability and automated deployment across many environments.
Benefits of cloud computing

Lower costs
IT cloud computing helps lower the large capital expenditures needed to maintain IT systems. Businesses can significantly cut costs by utilizing the capabilities offered by the cloud provider instead of investing in pricey infrastructure. Businesses only pay for the services they utilize thanks to cloud providers' pay-as-you-go business model, which further lowers expenses.
Flexibility and collaboration
Employees can work from anywhere at any time since cloud data is instantly accessible over the internet. You can set up your virtual workplace from anywhere thanks to the cloud. By granting them access to the same files as outside vendors, it also enables teams to collaborate on a project from different places.
Business Continuity
In the case of an emergency or outage, your data is securely stored and safeguarded in the cloud. When the systems are back up and running, this facilitates getting back to work.
Competitive Advantage
Cloud handles a number of corporate functions, including software licensing, IT infrastructure maintenance, and data management training staff. As a result, it offers you a competitive advantage because it requires less time and money.
Scalability
Cloud computing enables businesses to quickly expand their user base from a small number to thousands. Businesses can scale their storage requirements based on their need that gives them flexibility.
Self-servicing Provision
End users can request compute resources for almost any type of workload. End users can now provision computing capabilities such as server time and network storage, eliminating the need for IT administrators to provision and manage compute resources.
Multiple Usage
With multi-tenancy, several clients can share the same apps or physical infrastructures while maintaining control over their personal information security and privacy. Cloud providers can serve several clients from the same physical resources by using resource pooling. In order to meet the needs of numerous clients, cloud providers need have sizable and adaptable resource pools.
Agility and Speed
Rapid application and service deployment is made possible by cloud computing, which enables developers to quickly create resources and test new concepts. This speeds up time to market by doing away with the requirement for laborious hardware procurement procedures.
What are the future trends?
Container technology popularity
Container technology will become more and more popular over time. Regardless of the parent hosting environment (cloud, hybrid, or on-premise servers), containers provide a separate virtual environment for developing and executing applications. In essence, it enables businesses to enhance their development capabilities by establishing small, isolated clouds inside their own infrastructure.
The use of virtual desktops
It will grow in popularity and acceptance. Without connecting the desktop to the actual client device, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) enables remote desktop picture streaming. Since apps and services may be readily distributed to a distant client without requiring complicated installation or configuration, remote worker productivity is a key use case for virtual desktop infrastructure.
Security technologies
It will advance to become edge-first and cloud-native. The decentralization of remote hosting and processing via edge infrastructure is a key component of cloud evolution. The edge is the next frontier, even if cloud computing was previously a priority for cybersecurity companies since shared resources entail shared security threats.
Cloud use cases
These involve communication and collaboration will be crucial.
Following the widespread transition to remote work in 2020, modernizing channels for cooperation and communication was one of the top goals. Businesses may connect remotely thanks to the cloud, which makes it easier to collaborate within and interact with customers externally. VoIP and cloud-based video conferencing aren't the only examples of this.
Serverless computing
Even outside of the tech industry, serverless computing will be a fascinating area of adoption. A form of enterprise IT design where code is separated and modular is made possible by serverless architecture. It is an execution model that is usually used for cloud computing Such that in which resources are allocated to each isolated module that too based on real-time demand. Serverless is usually only used by platform providers and IT organizations who need to guarantee the highest amount of downtime for their products.
Cloud will drive the broad use of AI
Demand for artificial intelligence (AI) is rising in all business verticals and horizontals. Adoption of cloud computing will depend on the availability of AI libraries, modelling engines, and algorithms stored in the cloud.
Conclusion
It is anticipated that this investigation of cloud computing's characteristics will increase its capacity to revolutionize your company. We've talked about its wide range of products, how to match them to your unique requirements, and the technology's bright future.
Better methods for developing goods and services, giving good customer support, and doing research will be easily made possible by the cloud in the future. Business executives that take advantage of cloud computing's possibilities will undoubtedly have an advantage over their competitors in this dynamic environment, whether it be in the software and tools selected or the business plans they implement.
It might be very difficult to choose the best cloud option for your company. It's simple to become overwhelmed by the abundance of possibilities, particularly when your company's needs are changing and becoming more specific. To help you make the best choice in this situation, you require cloud consulting services at Sterling Technolabs.

FAQs
Q: What is Cloud Computing and How Does It Work?
A: Users can pay for just the computing resources that they use with the cloud computing. This is what it makes computing resources available over the internet as needed. It gives users access to technological services as needed, doing away with the need to maintain physical resources like servers and data centres.
Q: What Are the Different Types of Cloud Computing?
A: Public, private, and hybrid clouds are the three primary categories of cloud computing. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and serverless computing are the four primary services that fall under these deployment patterns.
Q: What Are the Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses?
A: Increased performance and efficiency, greater flexibility and dependability, and reduced IT expenses are all provided by the cloud. Additionally, it enhances innovation, enabling businesses to integrate AI and machine learning applications into their strategy and get a quicker time to market.
Q: What Are Cloud Computing Services?
A: Servers, storage, database servers, networking, software, statistical analysis, and intelligence are examples of computer resources that are made available online as cloud computing services. Without having to handle physical resources directly, cloud computing services enable both individuals and enterprises to access computing resources whenever they need them.
Q: What Are the Challenges of Cloud Computing?
A: The major challenges in cloud computing are serves, technology, usage issues, data security, performance, control, expertise and much more that are seen when used.
Although it sounds complicated, cloud computing is a straightforward idea. It refers to keeping all of your crucial information, files, applications, and even servers on a huge web network known as the Cloud. It is hardly surprising that this forecast was made. It provides dependability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness-all essential for any business to expand and thrive.
Cloud technology computing is now the best means to offer enterprise apps and the go-to option for businesses looking to expand their infrastructure or introduce new ideas. Learn more about cloud computing by reading this cloud computing blog, which covers all you need to know, including its definition and frequently asked questions.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand, pay-per-use online access to computing resources, including virtual or physical servers, data storage, networking capabilities, software, application development tools, AI-powered analytical tools, and more. When it comes to scalability and flexibility, the cloud computing architecture outperforms traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Additionally, cloud computing can be separated into two layers that is front-end and back-end. The front-end layer is the layer that users usually interact with. This layer makes it possible for a user to use cloud computing applications to access data that has been saved in the cloud.
In simple terms, the on-demand provision of computer services, including servers, storage, database servers, networking purposes, software, and analytics, is known as cloud computing. Cloud-based storage enables remote file saving instead of storing data on a local storage device or proprietary hard disc. Because it offers cost savings, better productivity, speed and efficiency, efficiency, and security, cloud computing is a popular choice for both individuals and enterprises.
How does cloud computing work?
Through the internet, the client devices can access rented computer resources that include data, analytics, and cloud apps. all this is thanks to cloud computing. Cloud service providers own and run the network of distant data centers, servers, and storage devices that it depends on. The storage capacity, security, and processing power required to preserve the data users send to the cloud are the providers' responsibility.
Automation and virtualization technologies are key components of cloud computing. Through the use of software called a hypervisor, IT organizations can use virtualization to generate virtual instances of servers, storage, and other resources that enable numerous virtual machines (VMs) or cloud environments to operate on a single physical server.
This makes it easier for users to request and utilize cloud resources available. This is done by streamlining their abstraction and provisioning into logical entities. Without direct assistance from the cloud provider's IT team, users can provision resources, connect services, and deploy workloads with a high degree of self-service thanks to automation and related orchestration features.
Types of cloud services
Private cloud
Internal users can use private cloud services from a company's data center. An organization creates and manages its own underlying cloud architecture when using a private cloud. This paradigm maintains the administration, control, and security typical of local data centers while providing the flexibility and convenience of the cloud. OpenStack and VMware are two examples of private cloud suppliers and technologies.
To satisfy their regulatory compliance needs, many businesses opt for private cloud environments rather than public ones. Private cloud environments are frequently chosen by organizations such as government agencies, healthcare facilities, and financial institutions for workloads including sensitive data, medical records, intellectual property, private documents, personally identifiable information (PII), and financial information.
Public cloud
A third-party cloud service provider (CSP) provides the cloud service online. That too under the public cloud paradigm. Although many public cloud services offer long-term commitments, they are usually sold on a minute or hourly basis. Consumers just pay for the bandwidth of the cloud, data storage, and CPU cycles that they usually use.
Since public cloud services are easily scalable and elastic, most businesses have shifted parts of their computer infrastructure to the cloud. This allows them to adapt to changing workload demands. Customers are drawn to the public cloud by the promise of increased efficiency and cost savings by only paying for what they use.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud combines on-premises private cloud services. This is with public cloud services that include automation and orchestration between the two types of cloud. Businesses can use the public cloud to manage their daily demand spikes or workload bursts. They can also use it while running sensitive apps or important workloads on the private cloud.
Creating a unified, automated, scalable environment that utilizes everything that a public cloud architecture has to offer while retaining control over mission-critical data is the aim of a hybrid cloud. Beyond physical connectivity and cloud migration, hybrid cloud architecture now provides a cost-effective, adaptable, and secure environment that facilitates workload portability and automated deployment across many environments.
Benefits of cloud computing

Lower costs
IT cloud computing helps lower the large capital expenditures needed to maintain IT systems. Businesses can significantly cut costs by utilizing the capabilities offered by the cloud provider instead of investing in pricey infrastructure. Businesses only pay for the services they utilize thanks to cloud providers' pay-as-you-go business model, which further lowers expenses.
Flexibility and collaboration
Employees can work from anywhere at any time since cloud data is instantly accessible over the internet. You can set up your virtual workplace from anywhere thanks to the cloud. By granting them access to the same files as outside vendors, it also enables teams to collaborate on a project from different places.
Business Continuity
In the case of an emergency or outage, your data is securely stored and safeguarded in the cloud. When the systems are back up and running, this facilitates getting back to work.
Competitive Advantage
Cloud handles a number of corporate functions, including software licensing, IT infrastructure maintenance, and data management training staff. As a result, it offers you a competitive advantage because it requires less time and money.
Scalability
Cloud computing enables businesses to quickly expand their user base from a small number to thousands. Businesses can scale their storage requirements based on their need that gives them flexibility.
Self-servicing Provision
End users can request compute resources for almost any type of workload. End users can now provision computing capabilities such as server time and network storage, eliminating the need for IT administrators to provision and manage compute resources.
Multiple Usage
With multi-tenancy, several clients can share the same apps or physical infrastructures while maintaining control over their personal information security and privacy. Cloud providers can serve several clients from the same physical resources by using resource pooling. In order to meet the needs of numerous clients, cloud providers need have sizable and adaptable resource pools.
Agility and Speed
Rapid application and service deployment is made possible by cloud computing, which enables developers to quickly create resources and test new concepts. This speeds up time to market by doing away with the requirement for laborious hardware procurement procedures.
What are the future trends?
Container technology popularity
Container technology will become more and more popular over time. Regardless of the parent hosting environment (cloud, hybrid, or on-premise servers), containers provide a separate virtual environment for developing and executing applications. In essence, it enables businesses to enhance their development capabilities by establishing small, isolated clouds inside their own infrastructure.
The use of virtual desktops
It will grow in popularity and acceptance. Without connecting the desktop to the actual client device, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) enables remote desktop picture streaming. Since apps and services may be readily distributed to a distant client without requiring complicated installation or configuration, remote worker productivity is a key use case for virtual desktop infrastructure.
Security technologies
It will advance to become edge-first and cloud-native. The decentralization of remote hosting and processing via edge infrastructure is a key component of cloud evolution. The edge is the next frontier, even if cloud computing was previously a priority for cybersecurity companies since shared resources entail shared security threats.
Cloud use cases
These involve communication and collaboration will be crucial.
Following the widespread transition to remote work in 2020, modernizing channels for cooperation and communication was one of the top goals. Businesses may connect remotely thanks to the cloud, which makes it easier to collaborate within and interact with customers externally. VoIP and cloud-based video conferencing aren't the only examples of this.
Serverless computing
Even outside of the tech industry, serverless computing will be a fascinating area of adoption. A form of enterprise IT design where code is separated and modular is made possible by serverless architecture. It is an execution model that is usually used for cloud computing Such that in which resources are allocated to each isolated module that too based on real-time demand. Serverless is usually only used by platform providers and IT organizations who need to guarantee the highest amount of downtime for their products.
Cloud will drive the broad use of AI
Demand for artificial intelligence (AI) is rising in all business verticals and horizontals. Adoption of cloud computing will depend on the availability of AI libraries, modelling engines, and algorithms stored in the cloud.
Conclusion
It is anticipated that this investigation of cloud computing's characteristics will increase its capacity to revolutionize your company. We've talked about its wide range of products, how to match them to your unique requirements, and the technology's bright future.
Better methods for developing goods and services, giving good customer support, and doing research will be easily made possible by the cloud in the future. Business executives that take advantage of cloud computing's possibilities will undoubtedly have an advantage over their competitors in this dynamic environment, whether it be in the software and tools selected or the business plans they implement.
It might be very difficult to choose the best cloud option for your company. It's simple to become overwhelmed by the abundance of possibilities, particularly when your company's needs are changing and becoming more specific. To help you make the best choice in this situation, you require cloud consulting services at Sterling Technolabs.

FAQs
Q: What is Cloud Computing and How Does It Work?
A: Users can pay for just the computing resources that they use with the cloud computing. This is what it makes computing resources available over the internet as needed. It gives users access to technological services as needed, doing away with the need to maintain physical resources like servers and data centres.
Q: What Are the Different Types of Cloud Computing?
A: Public, private, and hybrid clouds are the three primary categories of cloud computing. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and serverless computing are the four primary services that fall under these deployment patterns.
Q: What Are the Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses?
A: Increased performance and efficiency, greater flexibility and dependability, and reduced IT expenses are all provided by the cloud. Additionally, it enhances innovation, enabling businesses to integrate AI and machine learning applications into their strategy and get a quicker time to market.
Q: What Are Cloud Computing Services?
A: Servers, storage, database servers, networking, software, statistical analysis, and intelligence are examples of computer resources that are made available online as cloud computing services. Without having to handle physical resources directly, cloud computing services enable both individuals and enterprises to access computing resources whenever they need them.
Q: What Are the Challenges of Cloud Computing?
A: The major challenges in cloud computing are serves, technology, usage issues, data security, performance, control, expertise and much more that are seen when used.
Although it sounds complicated, cloud computing is a straightforward idea. It refers to keeping all of your crucial information, files, applications, and even servers on a huge web network known as the Cloud. It is hardly surprising that this forecast was made. It provides dependability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness-all essential for any business to expand and thrive.
Cloud technology computing is now the best means to offer enterprise apps and the go-to option for businesses looking to expand their infrastructure or introduce new ideas. Learn more about cloud computing by reading this cloud computing blog, which covers all you need to know, including its definition and frequently asked questions.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand, pay-per-use online access to computing resources, including virtual or physical servers, data storage, networking capabilities, software, application development tools, AI-powered analytical tools, and more. When it comes to scalability and flexibility, the cloud computing architecture outperforms traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Additionally, cloud computing can be separated into two layers that is front-end and back-end. The front-end layer is the layer that users usually interact with. This layer makes it possible for a user to use cloud computing applications to access data that has been saved in the cloud.
In simple terms, the on-demand provision of computer services, including servers, storage, database servers, networking purposes, software, and analytics, is known as cloud computing. Cloud-based storage enables remote file saving instead of storing data on a local storage device or proprietary hard disc. Because it offers cost savings, better productivity, speed and efficiency, efficiency, and security, cloud computing is a popular choice for both individuals and enterprises.
How does cloud computing work?
Through the internet, the client devices can access rented computer resources that include data, analytics, and cloud apps. all this is thanks to cloud computing. Cloud service providers own and run the network of distant data centers, servers, and storage devices that it depends on. The storage capacity, security, and processing power required to preserve the data users send to the cloud are the providers' responsibility.
Automation and virtualization technologies are key components of cloud computing. Through the use of software called a hypervisor, IT organizations can use virtualization to generate virtual instances of servers, storage, and other resources that enable numerous virtual machines (VMs) or cloud environments to operate on a single physical server.
This makes it easier for users to request and utilize cloud resources available. This is done by streamlining their abstraction and provisioning into logical entities. Without direct assistance from the cloud provider's IT team, users can provision resources, connect services, and deploy workloads with a high degree of self-service thanks to automation and related orchestration features.
Types of cloud services
Private cloud
Internal users can use private cloud services from a company's data center. An organization creates and manages its own underlying cloud architecture when using a private cloud. This paradigm maintains the administration, control, and security typical of local data centers while providing the flexibility and convenience of the cloud. OpenStack and VMware are two examples of private cloud suppliers and technologies.
To satisfy their regulatory compliance needs, many businesses opt for private cloud environments rather than public ones. Private cloud environments are frequently chosen by organizations such as government agencies, healthcare facilities, and financial institutions for workloads including sensitive data, medical records, intellectual property, private documents, personally identifiable information (PII), and financial information.
Public cloud
A third-party cloud service provider (CSP) provides the cloud service online. That too under the public cloud paradigm. Although many public cloud services offer long-term commitments, they are usually sold on a minute or hourly basis. Consumers just pay for the bandwidth of the cloud, data storage, and CPU cycles that they usually use.
Since public cloud services are easily scalable and elastic, most businesses have shifted parts of their computer infrastructure to the cloud. This allows them to adapt to changing workload demands. Customers are drawn to the public cloud by the promise of increased efficiency and cost savings by only paying for what they use.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud combines on-premises private cloud services. This is with public cloud services that include automation and orchestration between the two types of cloud. Businesses can use the public cloud to manage their daily demand spikes or workload bursts. They can also use it while running sensitive apps or important workloads on the private cloud.
Creating a unified, automated, scalable environment that utilizes everything that a public cloud architecture has to offer while retaining control over mission-critical data is the aim of a hybrid cloud. Beyond physical connectivity and cloud migration, hybrid cloud architecture now provides a cost-effective, adaptable, and secure environment that facilitates workload portability and automated deployment across many environments.
Benefits of cloud computing

Lower costs
IT cloud computing helps lower the large capital expenditures needed to maintain IT systems. Businesses can significantly cut costs by utilizing the capabilities offered by the cloud provider instead of investing in pricey infrastructure. Businesses only pay for the services they utilize thanks to cloud providers' pay-as-you-go business model, which further lowers expenses.
Flexibility and collaboration
Employees can work from anywhere at any time since cloud data is instantly accessible over the internet. You can set up your virtual workplace from anywhere thanks to the cloud. By granting them access to the same files as outside vendors, it also enables teams to collaborate on a project from different places.
Business Continuity
In the case of an emergency or outage, your data is securely stored and safeguarded in the cloud. When the systems are back up and running, this facilitates getting back to work.
Competitive Advantage
Cloud handles a number of corporate functions, including software licensing, IT infrastructure maintenance, and data management training staff. As a result, it offers you a competitive advantage because it requires less time and money.
Scalability
Cloud computing enables businesses to quickly expand their user base from a small number to thousands. Businesses can scale their storage requirements based on their need that gives them flexibility.
Self-servicing Provision
End users can request compute resources for almost any type of workload. End users can now provision computing capabilities such as server time and network storage, eliminating the need for IT administrators to provision and manage compute resources.
Multiple Usage
With multi-tenancy, several clients can share the same apps or physical infrastructures while maintaining control over their personal information security and privacy. Cloud providers can serve several clients from the same physical resources by using resource pooling. In order to meet the needs of numerous clients, cloud providers need have sizable and adaptable resource pools.
Agility and Speed
Rapid application and service deployment is made possible by cloud computing, which enables developers to quickly create resources and test new concepts. This speeds up time to market by doing away with the requirement for laborious hardware procurement procedures.
What are the future trends?
Container technology popularity
Container technology will become more and more popular over time. Regardless of the parent hosting environment (cloud, hybrid, or on-premise servers), containers provide a separate virtual environment for developing and executing applications. In essence, it enables businesses to enhance their development capabilities by establishing small, isolated clouds inside their own infrastructure.
The use of virtual desktops
It will grow in popularity and acceptance. Without connecting the desktop to the actual client device, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) enables remote desktop picture streaming. Since apps and services may be readily distributed to a distant client without requiring complicated installation or configuration, remote worker productivity is a key use case for virtual desktop infrastructure.
Security technologies
It will advance to become edge-first and cloud-native. The decentralization of remote hosting and processing via edge infrastructure is a key component of cloud evolution. The edge is the next frontier, even if cloud computing was previously a priority for cybersecurity companies since shared resources entail shared security threats.
Cloud use cases
These involve communication and collaboration will be crucial.
Following the widespread transition to remote work in 2020, modernizing channels for cooperation and communication was one of the top goals. Businesses may connect remotely thanks to the cloud, which makes it easier to collaborate within and interact with customers externally. VoIP and cloud-based video conferencing aren't the only examples of this.
Serverless computing
Even outside of the tech industry, serverless computing will be a fascinating area of adoption. A form of enterprise IT design where code is separated and modular is made possible by serverless architecture. It is an execution model that is usually used for cloud computing Such that in which resources are allocated to each isolated module that too based on real-time demand. Serverless is usually only used by platform providers and IT organizations who need to guarantee the highest amount of downtime for their products.
Cloud will drive the broad use of AI
Demand for artificial intelligence (AI) is rising in all business verticals and horizontals. Adoption of cloud computing will depend on the availability of AI libraries, modelling engines, and algorithms stored in the cloud.
Conclusion
It is anticipated that this investigation of cloud computing's characteristics will increase its capacity to revolutionize your company. We've talked about its wide range of products, how to match them to your unique requirements, and the technology's bright future.
Better methods for developing goods and services, giving good customer support, and doing research will be easily made possible by the cloud in the future. Business executives that take advantage of cloud computing's possibilities will undoubtedly have an advantage over their competitors in this dynamic environment, whether it be in the software and tools selected or the business plans they implement.
It might be very difficult to choose the best cloud option for your company. It's simple to become overwhelmed by the abundance of possibilities, particularly when your company's needs are changing and becoming more specific. To help you make the best choice in this situation, you require cloud consulting services at Sterling Technolabs.

FAQs
Q: What is Cloud Computing and How Does It Work?
A: Users can pay for just the computing resources that they use with the cloud computing. This is what it makes computing resources available over the internet as needed. It gives users access to technological services as needed, doing away with the need to maintain physical resources like servers and data centres.
Q: What Are the Different Types of Cloud Computing?
A: Public, private, and hybrid clouds are the three primary categories of cloud computing. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and serverless computing are the four primary services that fall under these deployment patterns.
Q: What Are the Benefits of Cloud Computing for Businesses?
A: Increased performance and efficiency, greater flexibility and dependability, and reduced IT expenses are all provided by the cloud. Additionally, it enhances innovation, enabling businesses to integrate AI and machine learning applications into their strategy and get a quicker time to market.
Q: What Are Cloud Computing Services?
A: Servers, storage, database servers, networking, software, statistical analysis, and intelligence are examples of computer resources that are made available online as cloud computing services. Without having to handle physical resources directly, cloud computing services enable both individuals and enterprises to access computing resources whenever they need them.
Q: What Are the Challenges of Cloud Computing?
A: The major challenges in cloud computing are serves, technology, usage issues, data security, performance, control, expertise and much more that are seen when used.
Recent Posts
Transform your vision into reality with Custom Software Development
Get Started
Office Address:
743A, Gera’s Imperium Rise,Hinjewadi Phase II, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Near Wipro Circle, Pune- 411057, Maharashtra, India
Ai
Services
Technologies
Transform your vision into reality with Custom Software Development
Get Started
Office Address:
743A, Gera’s Imperium Rise,Hinjewadi Phase II, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Near Wipro Circle, Pune- 411057, Maharashtra, India
Ai
Services
Technologies
Transform your vision into reality with Custom Software Development
Get Started
Office Address:
743A, Gera’s Imperium Rise,Hinjewadi Phase II, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Near Wipro Circle, Pune- 411057, Maharashtra, India
Technologies
Transform your vision into reality with Custom Software Development
Get Started
Office Address:
743A, Gera’s Imperium Rise,Hinjewadi Phase II, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Near Wipro Circle, Pune- 411057, Maharashtra, India
Ai
Services
Technologies
Transform your vision into reality with Custom Software Development
Get Started
Office Address:
743A, Gera’s Imperium Rise,Hinjewadi Phase II, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Near Wipro Circle, Pune- 411057, Maharashtra, India
Ai
Services
Technologies
Transform your vision into reality with Custom Software Development
Get Started
Office Address:
743A, Gera’s Imperium Rise,Hinjewadi Phase II, Rajiv Gandhi Infotech Park, Near Wipro Circle, Pune- 411057, Maharashtra, India






